Git tips

Contents
1 Create a new repo in VS Code and push it to GitHub
# first, create a repo on the GitHub webpage
# then, add the remote in VS Code
git remote add origin https://github.com/XiaomoWu/<your-repo>.git
# create the main branch in VS Code
git branch -M main
# push the main branch to GitHub
git push -u origin main2 Go back to a previous commit and start new from there
Stash or commit your working tree
git checkout [commit].- You’ll be on a detached HEAD now (i.e., leaving the main branch).
git switch -c [new-branch-name]- If you want to make new edits, it’s recommended to create a new branch. As shown below, I was first at C4, and then
switched to Commit 2. From there, I created a new branch “test.” This is the resulting commit graph:
switchis a newly introduced command. It’s the same ascheckoutbut it’s used on branches.
- If you want to make new edits, it’s recommended to create a new branch. As shown below, I was first at C4, and then
(optional)
git restore .- If you’re on a test branch but want to discard all changes (e.g., you want to go to the latest commit without saving current changes), use the
restorecommand.
- If you’re on a test branch but want to discard all changes (e.g., you want to go to the latest commit without saving current changes), use the
git merge main.- When you’re happy with your test branch, it’s time to merge it to
main. First, make sure you’re on themainbranch. Then run the merge command. After resolving all conflicts, you can commit. - In the following figure, the last commit in
testis “commit test.” I merge it tomainand here’s the result.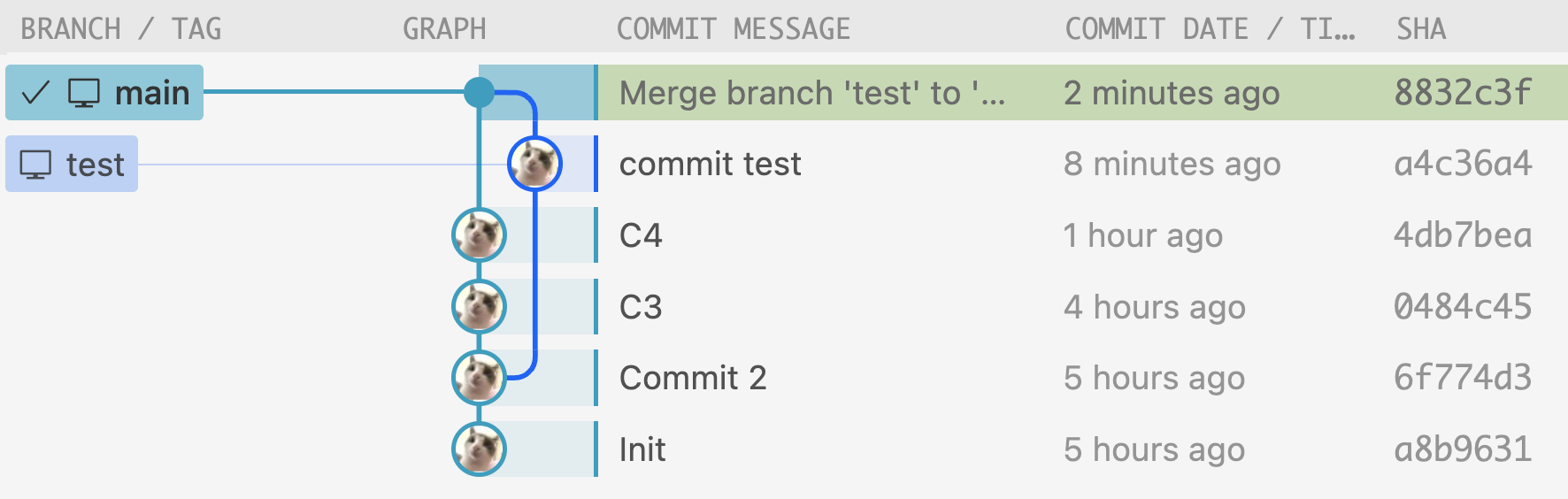
- When you’re happy with your test branch, it’s time to merge it to
Why not use "reset" or "revert"?
revert
revertdoes not take you to a previous commit. It only reverts the specified single commit.- For example, if your commit history is c1->c2->c3 (HEAD) and you revert c2, you may still keep changes introduced by c3!
- After reverting the given commit, it will compare your current state with the parent of that commit whose changes you are reverting. If the current state and that parent conflict, Git will indicate that.
- The
revertcommand requires your working tree to be clean (no modifications from the HEAD commit) (see documentation here).
reset
resetdoes take you to a previous commit, but you lose all the commits after the reset point.- Even if you use
--softinstead of--hard, you’ll still lose commits. The difference is that--softwill leave the changes to your work tree. - You may find yourself not losing commits after using
reset, but that’s only because you aren’t on themainbranch when youreset.
- Even if you use
switch
- Unlike
revertorreset,switchlands you on a totally detached branch. Whatever you do there has no impact on any existing commit. That’s why we useswitch. - If we need to keep our changes, just create a new branch and merge it to
main.